Optional Vaccines for Infants in India
 Vaccines are very critical during the growth of a child. You need to keep the child healthy free from infections. Become familiar with the importance of vaccination for a baby and the schedule during the growth in the previous article. Few are mandatory requirements for a baby in India and there are optional vaccinations recommended.
Vaccines are very critical during the growth of a child. You need to keep the child healthy free from infections. Become familiar with the importance of vaccination for a baby and the schedule during the growth in the previous article. Few are mandatory requirements for a baby in India and there are optional vaccinations recommended.
As a young mother understand the essentials for your baby. Consult with the doctor and take the necessary action.You may be worried to even visualize your baby going thru’ the pain of so many injections. With a little pain and healing your baby is going to enjoy a healthy tomorrow. In additional to the mandatory ones there are optional vaccines that has become a necessity in today’s world.
There are different diseases which can be deadly in children like polio, TB, Diphtheria, Tetanus, Measles, Hepatitis B. Giving vaccines for various Vaccines are given to babies to protect them and create acquired immunity to the disease. As is said Prevention is better than cure. Administer the vaccines in advance and prevent the babies from deadly diseases.
Following are the list of vaccines to be administered for your child. Make a note of all vaccines completed in your tracking card.Usually the peadiatrician or consulting doctor will give a card which has the vaccination schedule and the purposes, weight chart ,first aid and other simple remedies to be done at home.
At Birth Time:
1. Mandatory BCG (Bacillus Calmette Guerin)
Prevents: Tuberculosis
Important: Can cause slight swelling at the site of the injection, do not apply any medicine to the swollen area.
2. Mandatory OPV vaccine(Oral Polio Vaccine)
Prevents: Poliomyelitis (Polio) which damages nervous system, causes muscle weakness or paralysis.
Important: Given FREE in government centres upto the age of 5 years on Pulse Polio Immunization day
3. Mandatory Hepatitis B
Prevents: Liver infection caused by Hepatitis B virus
Important: Essential within 12 hours of birth to prevent transmission from mother.
4. Optional HPV(Human Papila Virus)
Prevents: Cervical cancer and other Genital cancers.
Important: Only for girls
Read: How to handle the new born baby
At 6 weeks (1.5 months old):
1. Mandatory DPT (Diphtheria, Pertrussis and Tetanus)
Prevents: Diphtheria(Upper respiratory illness), Pertrussis(whooping cough) and Tetanus
Important: There may be slight fever associated with pain and swelling at the injection site.
2. Mandatory OPV vaccine (Oral Polio Vaccine)
Prevents: Poliomyelitis (Polio) which damages nervous system, causes muscle weakness or paralysis.
Important: Given FREE in government centres upto the age of 5 years on Pulse Polio Immunization day
3. Mandatory Hepatitis B
Prevents: Liver infection caused by Hepatitis B virus
Important: The first and second dose of this medicine offer complete protection.
4. Optional HiB (Haemophilus Influenzae Type B)
Prevents: Menagitis, which affects membranes surrounding the brain and the Spinal cord.
Important: There may be slight redness, swelling or pain at the site of the injection.
5. Optional Pneumococcal
Prevents: Pneumococcal disease, caused by Streptococcous Pneumonia Bacteria
Important: Prevenar was the first vaccine against Pneumococcal disease in India.
At 10 weeks (2.5 months old):
1.Mandatory DPT (Diphtheria, Pertrussis and Tetanus)
Prevents: Diphtheria(Upper respiratory illness), Pertrussis(whooping cough) and Tetanus
Important: There may be slight fever associated with pain and swelling at the injection site.
2. Mandatory OPV vaccine (Oral Polio Vaccine)
Prevents: Poliomyelitis (Polio) which damages nervous system, causes muscle weakness or paralysis.
Important: Given FREE in government centres upto the age of 5 years on Pulse Polio Immunization day
3. Mandatory Hepatitis B
Prevents: Liver infection caused by Hepatitis B virus
Important: The first and second dose of this medicine offer complete protection.
4. Optional HiB (Haemophilus Influenzae Type B)
Prevents: Meningitis, which affects membranes surrounding the brain and the Spinal cord.
Important: There may be slight redness, swelling or pain at the site of the injection.
5. Optional Pneumococcal
Prevents: Pneumococcal disease, caused by Streptococcous Pneumonia Bacteria
Important: Prevenar was the first vaccine against Pneumococcal disease in India.
6. Optional IPV (Inactivated Polio Vaccine)
Prevents: Poliomyelitis (Polio) which damages nervous system, causes muscle weakness or paralysis.
Important: It eliminates the small risk of developing polio after receiving the live Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV).
At 14 weeks (3.5 months old):
1.Mandatory DPT (Diphtheria, Pertrussis and Tetanus)
Prevents: Diphtheria(Upper respiratory illness), Pertrussis(whooping cough) and Tetanus
Important: There may be slight fever associated with pain and swelling at the injection site.
2. Mandatory OPV vaccine (Oral Polio Vaccine)
Prevents: Poliomyelitis (Polio) which damages nervous system, causes muscle weakness or paralysis.
Important: Given FREE in government centres upto the age of 5 years on Pulse Polio Immunization day
3. Optional Pneumococcal
Prevents: Pneumococcal disease, caused by Streptococcous Pneumonia Bacteria
Important: Prevenar was the first vaccine against Pneumococcal disease in India.
4. Optional HiB (Haemophilus Influenzae Type B) / Meningitis vaccine MCV4 and MPSV4
Prevents: Meningitis, which affects membranes surrounding the brain and the Spinal cord.
Important: There may be slight redness, swelling or pain at the site of the injection.
5. Optional IPV(Inactivated Polio Vaccine)
Prevents: Poliomyelitis (Polio) which damages nervous system, causes muscle weakness or paralysis.
Important: Given in the form of injection.
At 6 months old:
1. Mandatory Hepatitis B
Prevents: Liver infection caused by Hepatitis B virus
Important: The first and second dose of this medicine offer complete protection.
Note: Some babies might get 4 doses, for example, if a combination vaccine containing hepatitis B is used. (This is a single shot containing several vaccines.) The extra dose is not harmful.
• Anyone through 18 years of age who didn’t get the vaccine when they were younger should also be vaccinated.
2.Optional Rotavirus
Prevents: Rotavirus infection which causes severe Diarrhoea among infants.
Important: First dose is given before the completion of 6 months and the second dose after a gap of 1 month.
3.Optional Influenza
Prevents: Influenza infection which causes infection of the respiratory system.
Important: The most common vaccine is Trivalent Influenza Vaccine ( TIV).
At 9 months old:
1. Mandatory Measles
Prevents: Measles, which causes infection of the respiratory system.
Important: Highly contagious disease. Hence it is very important to get the vaccination done on time.
At 12 months old (1 year) :
1. Mandatory Varicella
Prevents: Chicken pox.
Important: Varicella is the primary vaccine for protection against Chicken pox.
At 15 months (1.3 years old):
1. Mandatory MMR
Prevents: Measles, Mumps, Rubella
Important: There may be slight fever, joint pain or stiffness after the vaccination.
2. Optional Pneumococcal Booster
Prevents: Pneumococcal disease, caused by Streptococcous Pneumonia Bacteria
Important: Prevenar was the first vaccine against Pneumococcal disease in India.
3. Optional IPV(Inactivated Polio Vaccine)
Prevents: Poliomyelitis (Polio) which damages nervous system, causes muscle weakness or paralysis.
Important: Given in the form of injection.
At 18 months (1 .6 years old):
1.Mandatory OPV vaccine(Oral Polio Vaccine)
Prevents: Poliomyelitis (Polio) which damages nervous system, causes muscle weakness or paralysis.
Important: Given FREE in government centres upto the age of 5 years on Pulse Polio Immunization day
2. Mandatory DPT Booster(Diphtheria, Pertrussis and Tetanus)
Prevents: Diphtheria(Upper respiratory illness), Pertrussis(whooping cough) and Tetanus
Important: There may be slight fever associated with pain and swelling at the injection site.
3. Mandatory Hepatitis A
Prevents: Liver infection caused by HAV (Hepatitis A Virus)
Important: Since Hepatitis A is common in young Indian children, it is advisable to get this vaccination done.
4. Optional HiB Booster (Haemophilus Influenzae Type B)
Prevents: Meningitis, which affects membranes surrounding the brain and the Spinal cord.
Important: There may be slight redness, swelling or pain at the site of the injection.
At 2 years old:
1.Mandatory Typhoid
Prevents: Typhoid, a fever caused by Typhoid bacillus.
Important: There are 2 types of Typhoid vaccines: Inactivated vaccine (shot) and Weakened vaccine.
2. Mandatory Hepatitis A
Prevents: Liver infection caused by HAV (Hepatitis A Virus)
Important: Since Hepatitis A is common in young Indian children, it is advisable to get this vaccination done.
At 4 years old:
1. Mandatory MMR
Prevents: Measles, Mumps, Rubella
Important: There may be slight fever, joint pain or stiffness after the vaccination.
At 5 years old:
1. Mandatory OPV Booster(Oral Polio Vaccine)
Prevents: Poliomyelitis (Polio) which damages nervous system, causes muscle weakness or paralysis.
Important: Given FREE in government centres upto the age of 5 years on Pulse Polio Immunization day
2. Mandatory DPT Booster(Diphtheria, Pertrussis and Tetanus)
Prevents: Diphtheria(Upper respiratory illness), Pertrussis(whooping cough) and Tetanus
Important: There may be slight fever associated with pain and swelling at the injection site.
Consult the doctor on a regular basis to understand any updations in the vaccination schedule. Keep your little one free from infections and let her enjoy a healthy life for a healthy tomorrow.
Vaccines for your Baby – Immunization Schedule
 A lot of emphasis is mentioned by elders in administering vaccines for your growing baby. A new born baby has to follow the immunization schedule to remain healthy and free from infections. When the mother and child is being discharged from the hospital after birth, the baby’s doctor will give a briefing of the forthcoming immunization schedule and when to visit the hospital.
A lot of emphasis is mentioned by elders in administering vaccines for your growing baby. A new born baby has to follow the immunization schedule to remain healthy and free from infections. When the mother and child is being discharged from the hospital after birth, the baby’s doctor will give a briefing of the forthcoming immunization schedule and when to visit the hospital.
You may be worried to even visualize your baby going thru’ the pain of so many injection. The doctor responsible will hand over a tracking card which contains the proposed immunization schedule for reference and future action. Remember these are mandatory vaccines to keep sickness at bay. Understand which are the mandatory vaccines and how important the vaccines are for your baby.
Natural immunity for a baby
God has gifted every human with miracle fighters called antibodies which recognize anything that is ‘foreign’ to our body and destroy it. The greatest advantage is that the immunity system identifies these enemies that come back to attack and destroys them .In this way immunity is developed to the particular disease. The baby’s immunity is further improved by the mother’s breast milk in the first 4 to 6 months.
Then why to give vaccines for the baby?
There are different diseases which can be deadly in children like polio, TB, Diphtheria, Tetanus, Measles, Hepatitis B. Vaccines are given to babies to protect them and create acquired immunity to the disease. As is said Prevention is better than cure. Administer the vaccines in advance and prevent the babies from deadly diseases.
What is the immunization schedule and for what diseases?
Immunizations against common childhood diseases has been an integral component of mother and child health services in India since the adoption of the primary health care approach being reinforced by the Declaration of health Policy. Vaccines recommended by the Government and available in Government hospitals at reduced costs include:
BCG vaccine (mandatory) – Given as an intradermal injection soon after birth; prevents TB (Tuberculosis). Can cause slight swelling at the site of the injection, do not apply any medicine to the site. BCG : Bacillus Calmette Guerin
OPV vaccine (mandatory) – Given orally as several doses till the age of five, this prevents polio. Poliomyelitis is a disease which affects the nerves causing muscle weakness and paralysis. It is given free of cost to all children below five years of age under the Pulse Polio program. OPV: Oral Polio Vaccine
DPT vaccine (mandatory) – Given as an intradermal injection, it prevents three diseases Diphtheria, Pertrusis and Tetanus.
a. Diphtheria is an infection which starts with a ‘sore throat’ but can rapidly lead to formation of toxins (poisons) causing life-threatening complications.
b. Pertrusis (whooping cough) affects the lungs in children below 15 months of age. Starting with cold and cough, it progresses to episodes of coughs with a ‘whoop’. Complications include pneumonia, brain damage and death.
c. Tetanus starts when a wound is infected with bacteria found in soil, it affects the body’s muscles and nerves. The toxin produced by the bacteria causes muscle spasms, interferes with nerves and can be fatal.
Measles vaccine (mandatory) – The vaccine is given subcutaneously (just below the skin) as the baby completes nine months. A very contagious viral infection, measles starts as cold and cough with rashes progressing from the hairline downwards. It can progress to diarrhoea, pneumonia, infection of the brain leading to death, if untreated.
The immunization schedule as per the Universal Immunization Programme in India:
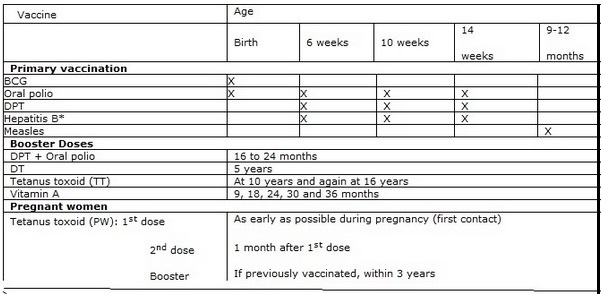 MMR vaccine (mandatory) – The vaccine is given as the baby completes 15 months. It prevents Measles, Mumps and Rubella. There may be slight fever, joint pain or stiffness after the vaccination.
MMR vaccine (mandatory) – The vaccine is given as the baby completes 15 months. It prevents Measles, Mumps and Rubella. There may be slight fever, joint pain or stiffness after the vaccination.
Note: MMR vaccine (mandatory) – The vaccine is given as the baby completes 4 years.
DPT Booster (mandatory) – The vaccine is given as the baby completes 18 months, it prevents three diseases Diphtheria ( upper respiratory illness), Pertrusis and Tetanus. There may be mild fever, pain & swelling at the injection site.
Typhoid (mandatory) – The vaccine is given as the baby completes 2 years, it prevents Typhoid, a fever caused by Typhoid bacillus.
DPT Booster (mandatory) – The vaccine is given as the baby completes 5 years, it prevents three diseases Diphtheria ( upper respiratory illness), Pertrusis and Tetanus. There may be mild fever, pain & swelling at the injection site.
Remember to complete vaccines on time and keep the nation free of diseases and the future generations in safe hands.









